Lean Startup: Achieve Success Quickly with Few Resources
Lean Startup addresses the issue of how to quickly develop a successful product without huge financial risk. This is not limited to startups – even well-established companies face this challenge. Market demand is a key focus of all companies. In an ideal world, every company would perform a comprehensive market analysis and develop a detailed product plan. But in today’s fast-paced market, is this really a viable strategy?
Lean Startup offers a slightly different way to address this problem. What is unique about this method? How does it work and which companies can profit from it?
The Lean Startup concept by Eric Ries
The Lean Startup method shares a lot in common with lean management. They both strive for quick, efficient processes with little waste. As the name suggests, Lean Startup was first presented as a solution for startups. Startups often face different challenges than established companies.
At the beginning, challenges lie primarily in allocating cash flow while avoiding financial risk. The goal is to develop a product that is in demand on the market and best meets customers’ needs.
Eric Ries developed the Lean Startup method to address these issues. He drew from lean management principles and in 2008, successfully introduced his idea. The Lean Startup method can be seen as a link between Design Thinking and agile methods.
It connects idea generation with rapid customer-oriented development without a long planning process. This is what makes Lean Startup a viable choice for any business looking to introduce or adapt a development process.
Is Lean Startup the right method for your business and what are the benefits?
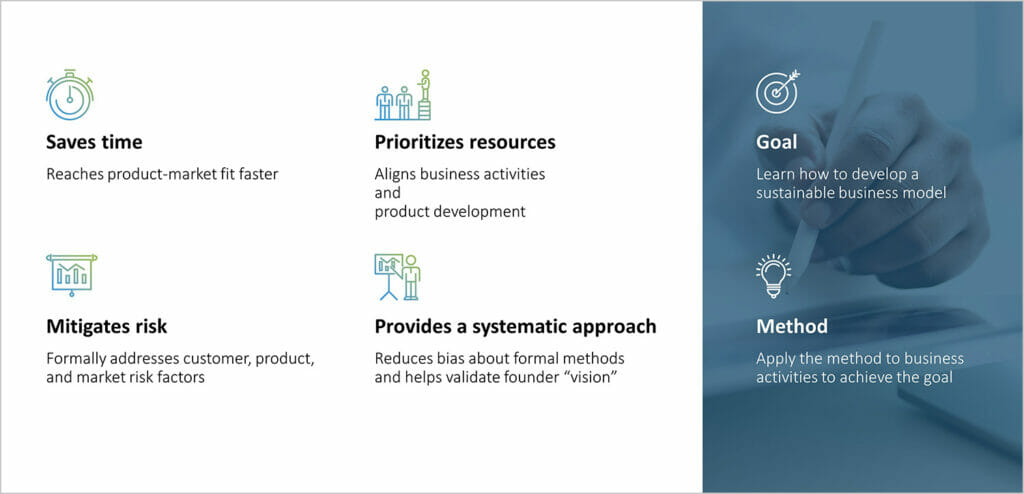
The benefits of Lean Startup include:
- It saves time: Short development cycles mean a quicker product-market fit. The product and its functions are optimized for the market.
- It minimizes waste: The Lean Startup method streamlines business activities and allocates financial resources efficiently.
- It reduces risk: By introducing a minimum viable product (MVP) to customers for feedback, companies can avoid high failure rates and reduce risk.
- It’s a systematic approach: Lean Startup’s clearly defined process involves learning through feedback and improving through metrics-driven testing.
- It provides a sustainable business model: One of the goals of Lean Startup is to develop a business model that guarantees sustainable growth and long-term competitiveness.
These benefits make it clear under how the Lean Startup method can work for your company. Every company wants to produce quickly, cost-effectively and with low risk, as well as develop a sustainable business model.
But like any other business model, Lean Startup does have some limitations.
Before getting started, there are often legal questions coupled with concerns about competition, for instance, how to protect intellectual property. Many entrepreneurs also worry that short development cycles and an immature product could make them vulnerable to competitors’ brand strength. Team morale can also present an obstacle. Lean Startup thrives on learning from mistakes and retesting the development cycle with knowledge gained from previous iterations.
This can have a negative impact on employee morale and fuel a fear of failure. At this stage, it’s important to reiterate the importance of trusting the process. Communicating the strategy transparently is the most effective way to address the concerns of your team.
Finally, successful Lean Startup depends on the nature of your business and the market you want to succeed in. For example, small businesses that focus on serving the founder’s lifestyle rather than earning high capital gains are generally less suited to the Lean Startup method. This method is more attractive to large companies and scalable startups, as it focuses on growth and the need for innovation.
Before deciding on Lean Startup, you need to take a look at your company’s positioning and its target market. The method is most effective in new, rather than existing markets. Once you have decided on Lean Startup, the next question is: How can we implement it successfully?
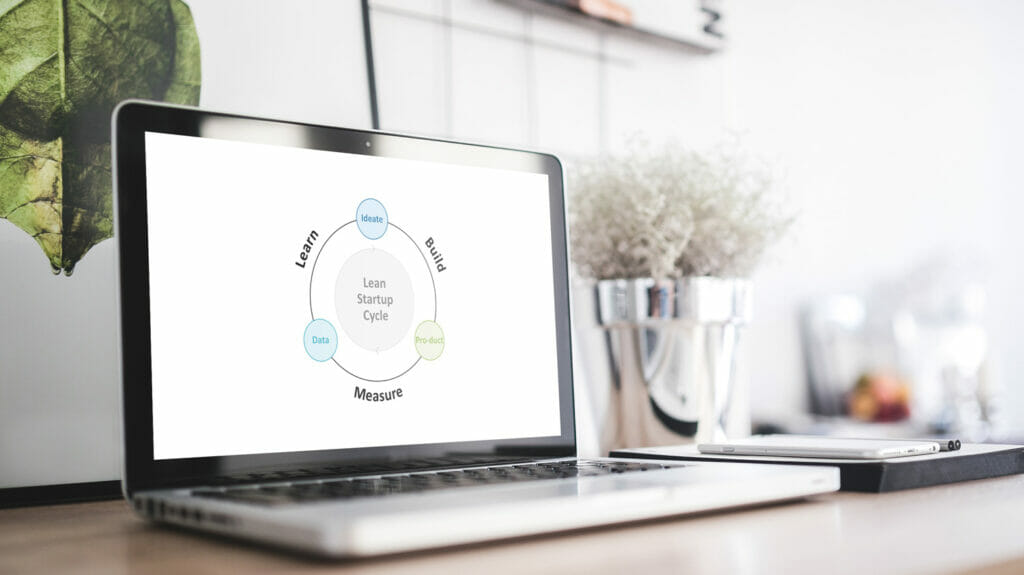

The Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop
At the heart of the methodology is the Build Measure Learn feedback loop which illustrates the iterative nature of Lean Startup. It illustrates the iterative process of Lean Startup. As its name suggests, customer feedback is a key component. The cycle can be continually adapted using this feedback and the knowledge gained from it. The process starts with the Build phase, followed by Measure and Learn.
The process can also be seen as a test of hypotheses. Each idea and its implementation represents a hypothesis about the product and market. With the market launch, data is collected and used to analyze and interpret the hypotheses. the final step, Learn, the hypotheses are verified. If the evaluation is negative, the hypothesis must be adapted and checked in a new test run.
- Build
In the first phase of the cycle, everything revolves around the future product. The focus is on how to develop a product that can meet market demand and excite the customer. There is no long and costly market research or detailed planning. Rather, the focus is on finding a solution that doesn’t waste time or resources – the minimum viable product (MVP). It’ s not about producing a perfect product; the primary goal of this phase is to bring the product to market quickly and in doing so, minimize the process throughput time.
The product ideas are usually limited to just a few functions that can solve customers’ problems and provide value. In a nutshell, a prototype is developed to gain customer feedback for further development steps. Once this prototype is developed, it’s time to move from the Build phase to the Measure phase.
- Measure
This is when customer feedback and reactions are collected. This data can be used to analyze and evaluate the product idea and its practical implementation. The most valuable data points out errors and problems, which then lead to opportunities for improvement. The scope of this data can be limitless.
To keep this phase of the loop short, parameters for the data should be defined and set prior to market launch. The organization needs to decide which customer reactions are important and how to interpret these reactions. This can then be used to generate insights in the Learn phase.
- Learn
The Learn phase is about validated learning. Assumptions about the product are checked against the collected data. The blind assumptions made at the beginning of the process are replaced by hypotheses. If these hypotheses can’t be validated, they can be adapted when the loop is restarted. This Lean Startup phase determines how the company should proceed. The information about the product can be used to determine whether the chosen path is the right one.
Lean Startup offers two options at this point: Continue development or start from scratch. This second option is called a pivot. The loop allows you to abandon course and reorient yourself. This promotes innovation and ensures that the company remains true to its customers.
Gaining knowledge with the minimum viable product (MVP)
A product must be developed for market launch before the Build-Measure-Learn loop can even begin. A prototype is quickly built to minimize production cycles and costs. The prototype addresses the target group’s most pressing problem while still having the potential to be further developed.
This means that the product should contain only a few basic functions. Before developing an MVP, the company needs to identify the most important problems of the customer group. Then a solution-oriented product can be developed. The MVP can be characterized as follows:
Minimum: The most stripped-down solution to the problem.
Viable: The solution provides enough features to satisfy early adopters.
Product: Something tangible that customers can touch and feel.
The core task of the MVP in Lean Startup is to generate maximum data to gain knowledge with minimal effort. The MVP does not claim to be a finished product and shouldn’t be considered one. The MVP will ultimately be further developed or realigned with the knowledge gained during the Learn phase and then tested again.
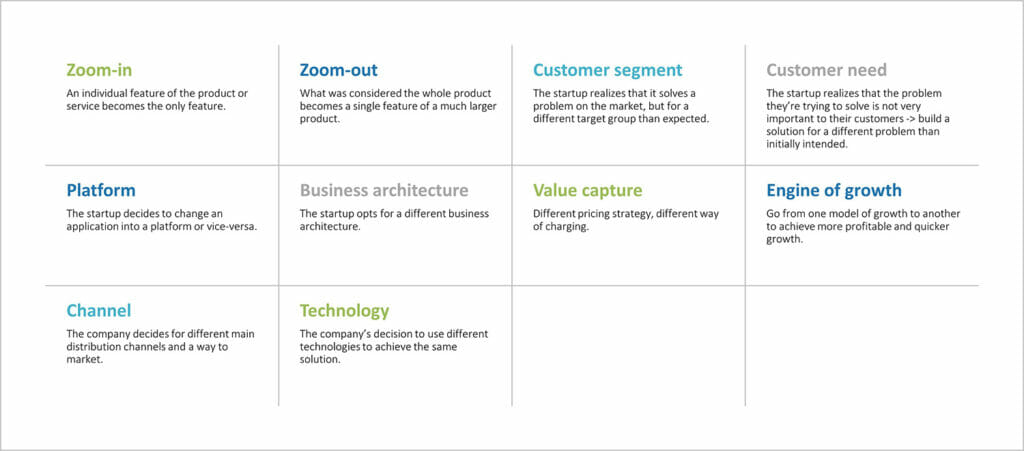
Stay the course or start from scratch: When should you pivot?
The decision to continue with the previous strategy or pivot is made after the first complete loop. In a pivot, the process is reset, and a new MVP starts the Lean Startup development loop. This decision should be based on key figures and facts. A pivot doesn’t turn the development process into a one-way street. A pivot always creates new paths and opportunities.
Models and diagrams that support Lean Startup
In addition to the pivot and the Build-Measure-Learn loop, there are other concepts and models that help implement the Lean Startup approach.
Lean Startup’s key points are:
- to identify the most immediate problems of the target customer group
- to position the company
- to identify the characteristics of the market you want to enter.
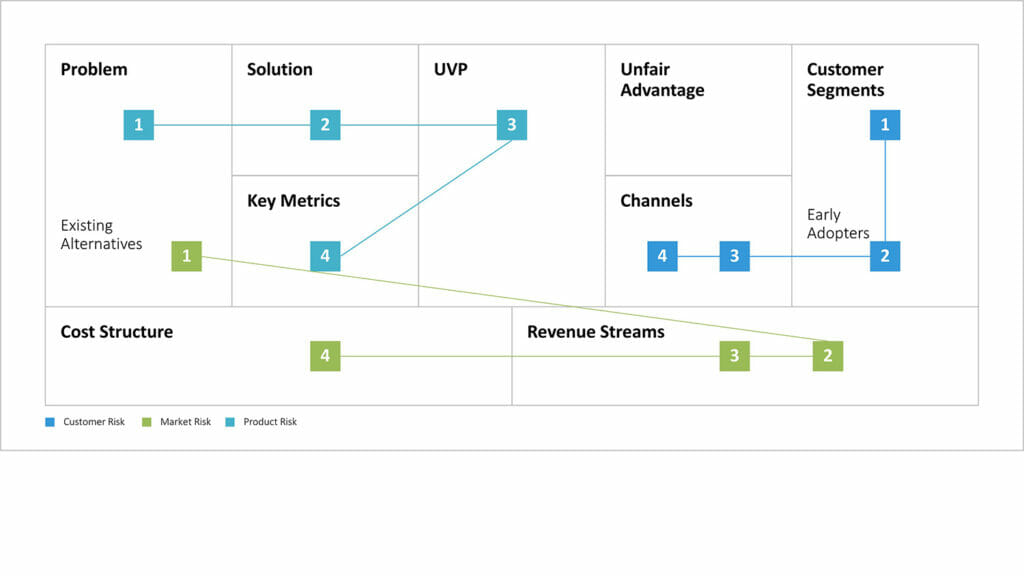
The first two points can be explored using a Business Model Canvas or Lean Canvas.
The Business Model Canvas comprises of blocks that contain essential elements of a company. Examples include the unique value proposition, the target group and its problems, key performance indicators, cost structures and the channels used.
The Lean Canvas is particularly suited to startup companies as it focuses even more on the central aspects of an organization. It is a more condensed version of the business model canvas.
Both models can be presented in a PowerPoint template and filled with individual content. A PowerPoint template allows the models to be presented to employees and decision-makers, and ensures all stakeholders are up to date on how Lean Startup is being implemented in the organization.
PowerPoint also offers the possibility to adapt the Lean Startup models and diagrams to your corporate design, guaranteeing a professional and consistent presentation. The iterative processes of the Lean Startup method, such as the Build-Measure-Learn loop, require regular updates and changes. Ready-made Lean Startup templates for PowerPoint make this easy.
Visualize with PowerPoint
PowerPoint can be used to visually present both models and add individual company content. Using PowerPoint allows the models to be presented to employees and decision makers. It creates a company-wide understanding of the current situation and goals, providing the foundation to successfully implement Lean Startup in the company.
Working with PowerPoint also offers the possibility of adapting Lean Startup models and diagrams to your corporate design. A uniform and professional design is guaranteed. The iterative procedures of the Lean Startup method, such as the Build-Measure-Learn loop, require regular updates and changes to slide content. PowerPoint is the perfect application for these quick and small adjustments. Continuous editing of your models and canvas is easy with ready-made Lean Startup PowerPoint templates.
Professionally designed templates from PresentationLoad can be found here:
Summary:
Lean Startup is not just for startups – established companies can also benefit from this method. In particular, the iterative approach of the Build-Measure-Learn loop ensures maximum innovation and flexibility. Lean Startup not only supports founding a company and product development, it also offers numerous possibilities to visualize company goals and strategies. This leads to a better understanding of existing measures and increases the company’s chances of market success.
Are you looking for PowerPoint templates for your Lean Startup presentation? You can find professionally designed templates here.
Do you have questions about the Lean Startup method or need help with your PowerPoint presentation? Then feel free to contact us at [email protected].